
- #PREFLIGHT MISSING ALLOW ORIGIN HEADER AXIOS FULL#
- #PREFLIGHT MISSING ALLOW ORIGIN HEADER AXIOS SERIES#
With these modifications in the calls and the proxy settings, we are now ready to develop our application calling any API using Axios without CORS problems. Already in the app.vue file itself we can add an example method to make a Get type request with Axios to our example API: const searchFromApi = async ( query : string ) => Īs you can see, the API call is made using as url the reference made in the file and not the API url. To create a test project (I will not go into detail) it is necessary to execute the following commands: yarn create vite // framework: vue // variant: vue-ts cd vite-project yarn yarn add axios yarn devĪs always, when calling the dev URL (in our case localhost: 3000) the typical Hello World landing appears. Introductionīefore going in depth, I leave a small summary of the characteristics of the project: In today's article we will talk about CORS, Proxies with Vite, and redirects with Netlify.
#PREFLIGHT MISSING ALLOW ORIGIN HEADER AXIOS SERIES#
However, along the way I am finding a series of differences that I find interesting to comment on. I created this project with Vite and Vue 3 to test the new features that it brings with respect to the previous version. Lately I have been working on a personal project that among other things uses a SERP service through an API. He's also taught programming to many graduates, helping them become better future developers.You can read this article also in Spanish. Siddhant has a passion for teaching and a knack for writing. He’s worked with scaling multiple startups in India and has experience building products in the Ed-Tech and healthcare industries.
#PREFLIGHT MISSING ALLOW ORIGIN HEADER AXIOS FULL#
Siddhant is a full stack JavaScript developer with expertise in frontend engineering. Make sure you have a foolproof server side fix to the problem before you deploy your application. Lastly, be aware that most of the tricks and hacks on the client side will not work in production.
Always remember to give a mode property with the value cors inside your fetch requests. You can even use chrome plugins like CORS Unblock to achieve this. Here's a useful guide that can help you out in that context. This may require some extra effort at first, but it definitely can be worth the investment. You can even create your own proxy server and serve requests through it. If you're running out of time, you can set up a proxy for your React app for development. Next time you run into the CORS error, remember to handle it first on the server side. Go inside your app's package.json file and add the following property: Have you ever tried to proxy your classmate during a lecture by shouting out to their roll call? That's how proxying works in API requests as well! You can tell your React app to proxy your requests to a server using the proxy property inside the package.json file.


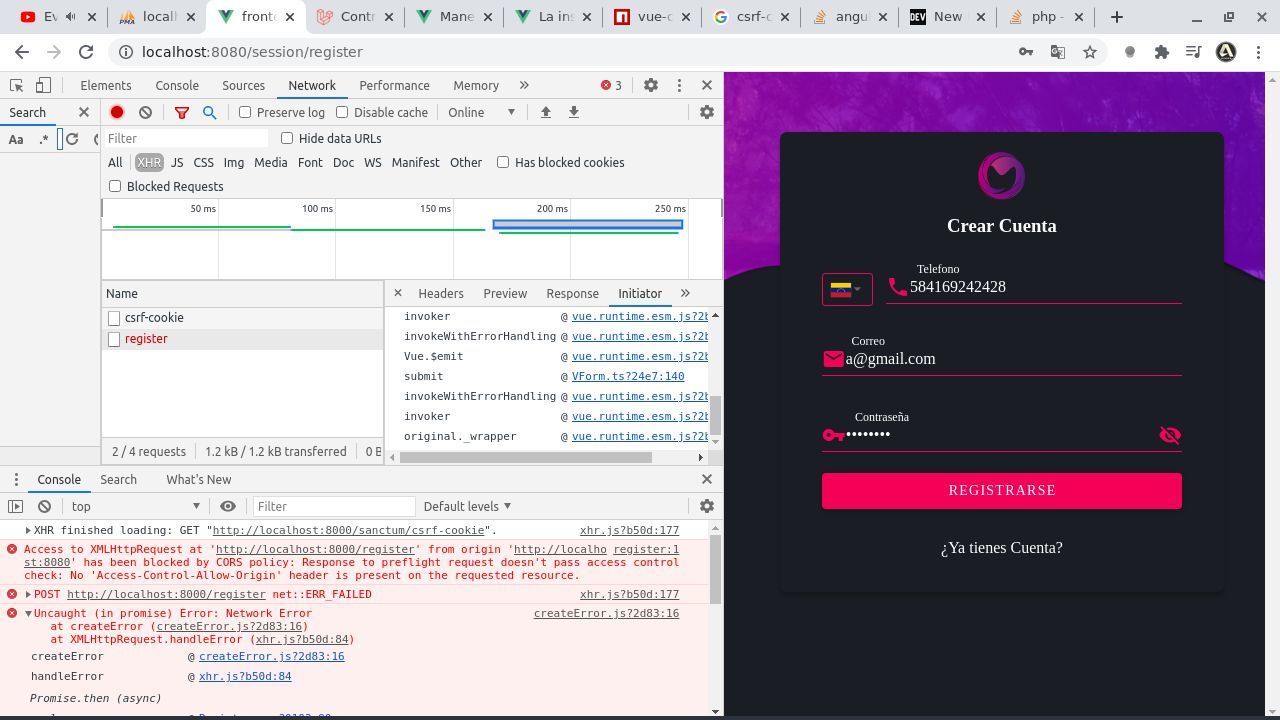
There's a neat trick specific to React apps that you can use to work around this problem. In such cases, there isn't much you can do but shoot an email to the developers asking them to enable CORS for your app. In some cases, you might not have access to server-side code.įor example, if you're using a third-party service for authentication, notification, sending emails, etc., you might run into this problem. It requires you to make modifications on the server side. While the server-side fix to CORS is the most technically coherent solution to this problem, there's a small catch. Let's head back to our server's app.js file.Īpp.get('/cors', (req, res) => ) Later we'll explore a way to work around this on the client side, but the most reliable solution is to always make the response from the server CORS-friendly. Hence, logically, CORS should always be handled from the server side. Therefore, it makes sense to configure the response from the server in such a way that the browser identifies this as a CORS request. It's only something that your browser imposes, and it suggests that your requested resource should be configured differently. If you think about it, your client doesn't have anything to do with CORS. It states that there's a missing Access-Control-Allow-Origin header on the resource you requested.
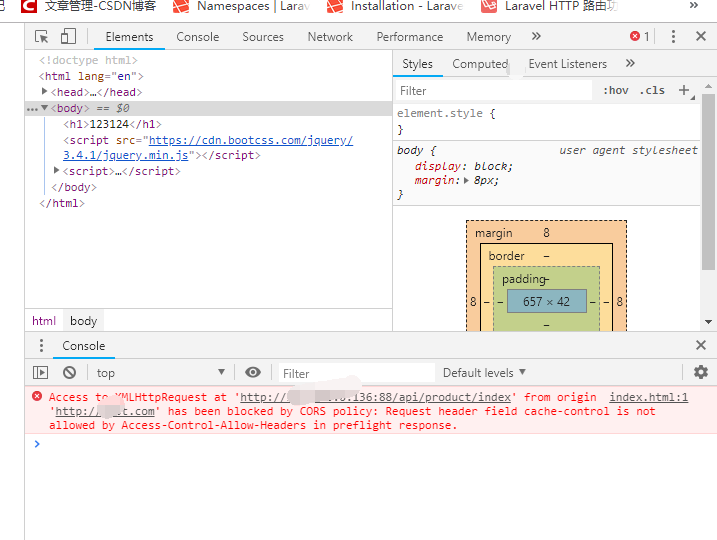
If an opaque response serves your needs, set the request's mode to 'no-cors' to fetch the resource with CORS disabled. Access to fetch at ' from origin ' has been blocked by CORS policy: No 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header is present on the requested resource.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
